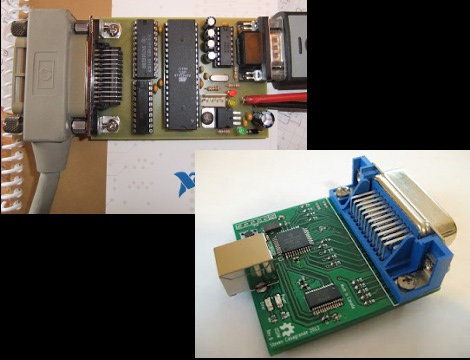
Dust off that old GPIB hardware and hook it up to your modern computing platform using either of these two solutions. If you haven’t a clue what we’re talking about you probably don’t own any fifty-year-old test equipment. But the General Purpose Interface Bus (aka IEEE-488) was fairly common on 1960’s era test equipment like multimeters and logic analyzers.
[Sven Pauli] is responsible for the RS232 GPIB interface board (translated) in the upper left. It uses an ATmega16 and a couple of classic bus driver chips to get the job done.
To the lower right is a USB to GPIB converter board that [Steven Casagrande] developed. This one is PIC based, using the 18F4520 and an FTDI chip to handle the USB side of the equation.
Check out the connector that is used for this protocol. We’d bet that’s not the easiest part to source. But at least now you’ll know what you’re looking at when pawing through the flea market offerings.




Hmm, I still use GPIB (under Visa) when putting together new test stations with modern equipment. There are a couple commercial USB to GPIB options, though, which are essentially no more expensive than just the GPIB cables themselves. Automatically searching for a device on a GPIB bus tends to be a better option than trying to figure out what COM port and baudrate that device you just plugged in is running at.
Just want to say that GPIB is still common even in modern test equiqment.
kcsaff beat me to it. GPIB had a lot longer run than just the 60s. It was mainstream through the 80s. And it was used for a lot more than just instruments including printers, plotters, controllers and disk/tape drives. It was actually a lot of fun to use. HP did a fantastic job of integrating it all together and you could quickly write really cool software on their lab controllers. Nothing like watching a mechanical plotter plot out the data you just acquired from an experiment controlled and measured using pricey HP gear.
$60 for a USB to GPIB is a sweet deal… I’m used to paying $150 for the commercial adapters.
There is a company on ebay that sells USB-GPIB adapters for $45.
http://www.ebay.com/itm/USB-to-GPIB-Interface-/251049611233?pt=LH_DefaultDomain_0&hash=item3a73b90fe1#ht_500wt_1276
I have a GPIB based Radoma Spectroradiometer that uses GPIB. Been thinking about something USB to get rid of the massive cable between my computer and Spec. Make it a little more portable too.
There are a number of issues I have with that adapter. Connectivity is limited to “Windows 98/W2K/XP”. There is no list of commands so that you may create an automation script. Downloading binary data from your instrument would be a pain.
For $15 extra, you get an OSHW adapter, that is made in Canada, and provides you with the means to use it how you like!
Open Source means nothing to me and probably 99% of others. And virtually all the software for tools is on windows anyways so it really does not matter if it is cross platform compatible.
Will yours just show up in the Nat Inst software?
Though I would probably end up getting this one. Having a non-exposed board is a plus for me:
http://www.ebay.com/itm/Low-Price-82357B-GPIB-USB-Interface-/261014428881?pt=BI_Control_Systems_PLCs&hash=item3cc5ac1cd1#ht_3346wt_1261
Open Source has nothing to do with cross platform. It has to do with the ability to adapt and modify it.
I never said it did. Those were two different subjects.
I agree that OSHW means nothing to the majority of the population, but I do not believe your guess of 99% for my target audience: hobbyists and scientists.
You may not think that Linux compatibility is important, but a significant portion of the people who have my adapter are running some version of Linux. At the laboratory, we run Linux on the computers for several experiments. Generally, only when we are forced to by software constraints will you find Windows at our lab. This is not the case in all our University labs, but after touring many over the years, I would say its still a significant percentage.
For your other question: No it will not as it is not VISA compatible.
Glad to hear $60 works! I wanted something priced affordable for hobbyists as well as professional.
Those connectors are standard centronics connectors. They were common on parallel printers in the 90s. They are still readily available at digikey…hell they have a whole product category devoted to them…
http://search.digikey.com/us/en/cat/connectors-interconnects/d-shaped-centronics/1442712
I guess these guys have never seen a real parallel port before.
No they aren’t. Centronics has 36 pins. IEEE-488 has 24 pins.
No retard. That style of housing is called centronics, the pin count is irrelevant. Serial connectors are 9 pin D-Sub, does that make the 24 pin D-Sub not a D-Sub…NO. Take a look at digikey for yourself.
The ‘housing’, as you call it, is called ‘micro ribbon connector’.
The term ‘Centronics’ is the name of the company that developed the standard now known as ‘IEEE-1284’. This standard also specifies a variant ‘Type A connector’ being a 25-way SUB-D connector.
HPIB was developed in the early 1970s, then adopted and designated as IEEE-488 in 1975. It is still widely used, although LXI, an Ethernet-based successor bus for instrumentation, has been in the works for a few years (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LAN_eXtensions_for_Instrumentation).
Jumping on the bandwagon with GPIB’s not dead – every new piece of RF test equipment I’ve seen has GPIB, and we certainly used it for everything
GPIB enables you to do some of the coolest things. If you have a bench top multimeter with a GPIB port and it can read samples fast enough you can use it as current scope.
I also know some one that has made his own ethernet to GPIB adapter and uses it to automate testing radio equipment he makes and sells. He just plugs the radio into his test set up, enters a serial number, waits, and then unplugs it when its done. He then has a report complete with digitized spectrum analyzer screen shots on each unit he sells.
I used EEE-488 for test equipment we were developing for the Navy in the late ’80s. Nice to see it is still being used.
we’ve paid £400 for our GPIB interfaces. faily sure they were agilent and when you’re spending £30k on a bit of test gear, and £3k for test fixtures, the £400 doesnt sound too bad…
until you see the ebay prices that is
Those NI/Agilent ones are nice. They support the high-speed protocol, parallel polling, etc. But, it’s well outside the realm of reasonable for hobbyists, and even most scientific research groups.
Just remember that at least the first one can not have a second controller on the same bus, because it can not free the bus quick enough.
Remember that the second one can’t either. It just silently neglects it. Nor does it proper treating to line endings. It does not even feature I/O buffering or proper line drivers.
I suspected it did the same, but couldn’t verify that for sure.
This is true, my adapter does ignore other controllers. I never thought that this would come up. If enough people need that I will add it in at a later date. However, as it stands, there are more important things to do than add such a small feature.
Could you elaborate on your I/O buffering concern? Currently 1 command from the PC is buffered at a time. In the future I plan on changing that into a FIFO queue. Feel free to email me your suggestions, it would be much more helpful to everybody than what you have posted.
Driver chips will be in a future hardware revision.
The same applies to me as well. I simply do not need the multi-controller feature.
On buffering, the point is two issues. First you’re using gets(), which is a perfect thing for software suicide. It just provides no prevention from buffer overflows and such. Further, two successive commands with little delay in between will break your reception. You can easily avoid this by only doing the gets() if newCmd is cleared in the ISR.
Thanks for the tips! I’ll take a closer look when I get home tonight. I agree that gets() isn’t the best idea. However, I’m looking to improve that entire routine with a FIFO queue, which will require replacing gets(). That will all be done together to avoid wasting time.
Any details on your line ending comment? I’m not sure what you mean there either.
Adding my “not dead yet” to the list, most of our new test equipment has GPIB ports on it as well, bench top scopes, multi-meters, muxes, power supplies, and our Fluke Power Calibration standards all use it.
We’ve started moving from the USB/Serial converters over to NI’s Gig-Ethernet to GPIB adapters, they work great, but have a hefty price tag. 🙁
I plan on eventually making an Eth-GPIB adapter. Most of the microcontroller code ports right over, so it’ll be pretty straight forward.
First, selling enough usb->gpib adapters to afford more r&d!
or bundle Gigabit wifi router with USB like TL-WR1043ND
So, the gross majority of “inexpensive” (a hobbyist myself griping at my $100 NI-PCI off of eBay) have massive problems…
-1. No VISA support, so you have to write everything from the ground up.
-2. No polling.
-3. No bus driver chips! None of the USB adapters can ever drive a cable, and if they can, it often has to be kept short…
Now, the VISA license is not that bad, and a hobbyist (or Sparkfun, etc.) could easily make a -real- GPIB interface to USB, but nobody’s done it yet. I’ve thought about it.
Considering the price of new GPIB cables it is probably cheaper to put on one adapter per unit, especially for longer runs.
Hi Tyler,
1) That isn’t that much work. I’ve already made a generic instrument python class to handle all the backend stuff. If one wants to use python, all they have to do is use my class.
2) Polling hasn’t been programmed yet, but will be in the near future. I have a volunteer from the UK to help me with that.
3) I’ve tested my adapter at the lab with a few instruments hooked up to several meters of cable. Everything worked fine. However, I do understand the correct driver chips are important, and will probably be included in the eventual revC.
My adapter was never meant to be a total replacement for the $600 NI/Agilent/other ones. It’s meant to handle most of the issues a hobbyist will come across for a fraction of the price.
Well, I wanted to make an interface that operates as compatible as possible with the features provided.
So I *do* use proper bus driver IC and I *do* have prepared the firmware for polling. At least, if I understood it properly from my quite ol’ books. Older than me 🙂
But I don’t know VISA and the NI stuff in depth. I could, however, imagine, that there is a kind of generic driver to operate with the ‘Universal Language Interface’ that is also supplied with the old DOS drivers from NI. So basically, it might show up and work in VISA as well. I unfortunately have no chance to check with a working VISA setup :-/
I didn’t know about GPIB until a couple of weeks ago when a friend gave me a pile of unwanted computer parts taken from working setups and told me to drop them on eBay. The Allen Bradley PCI boards got snapped up pretty quick and the NI GPIB PCI boards have quite a few watchers, quite curious to see what they finally go for.
I remember reading a couple of years back someone complaining about why RS232 serial devices were still around when we had this ‘shiny new’ plug’n’play interface called USB. I guess they’ve never written a line of code or held a soldering iron in their life!
Our lab at work has devices that use GPIB and HPIB which was the original Hewlett Packard proprietary protocol that was adopted to eventually become GPIB (IEEE-488). It’s annoying to have both protocols on the same bus because you’ll have a bit of a headache scanning the bus for all devices unless you’re crafty about it.
So yeah, LAN is the way to go. GPIB only has something like 9600 Baud maximum anyway if memory serves (?).
” If you haven’t a clue what we’re talking about you probably don’t own any fifty-year-old test equipment. But the General Purpose Interface Bus (aka IEEE-488) was fairly common on 1960′s era test equipment like multimeters and logic analyzers.”
GPIB direct to PCI/PCIe bus is still alive and well. It’s used where you want dedicated, bulletproof instrument connections. Ethernet is also good. USB connections aren’t as reliable; I always opt for Ethernet or GPIB over USB in my test system designs.
I’m tired of some youngster at HaD talking like such and such thing is “old” when nothing could be further than the truth. Why don’t you do a little research before outright deprecating something.