Nearly everything at [HAD] is at least based on science in some way or another. If, however, you would like to do some actual scientific experiments with stuff around the house, [Observationsblog] might be for you.
The particular posts that [Ken] wrote in to tell us about were all about acids, bases, and natural indicators. In his first post he goes over some definitions of acids, bases, and what pH exactly means. A good refresher for those that have forgotten some of their high school (or college) chemistry classes.
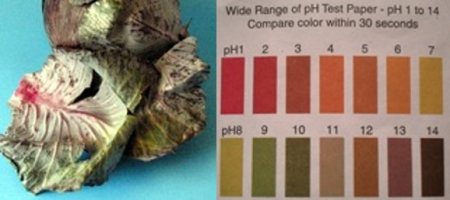
The other two posts have to do with making your own natural acid/base indicators. The first is called Anthocyanin, and can be extracted from Red Cabbage. Quite specific directions can be found here. Similar directions can be found to turn the Indian spice of [Turmeric] into an indicator as well. Although these concepts probably won’t help build your next robot, they could easily be copied inspire young minds for a great science fair project!






Recent Comments