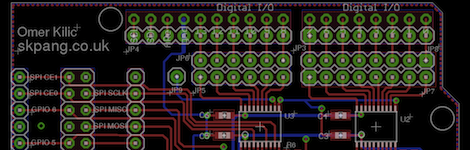
Since the Arduino was launched years ago, many ‘shields’ or add-on boards providing additional functionality have been released. There are hundreds of different shields, from video capture shields to touch screen shields. Now that the Raspberry Pi is out in the wild, it was only a matter of time before a RasPi to Arduino shield bridge was created.
[Omer] calls his bridge ‘Ponte’ and it allows Arduino shields to be used with the incredible horsepower of an embedded Linux system. While [Omer] originally expected to write the RasPi to Arduino software converter himself, but found WiringPi halfway through the build. Of course this build comes just a day after we saw a tutorial on controlling the GPIO pins on the RasPi, and we expect to see similar GPIO-hacking builds in the future.
Right now, the Ponte only supports Arduino Uno-sized shield, so the possibility of an all-in-one RepRap controller using the RAMPS motor driver is impossible for now. We expect that to change very quickly as more people get their RasPis delivered.









Recent Comments