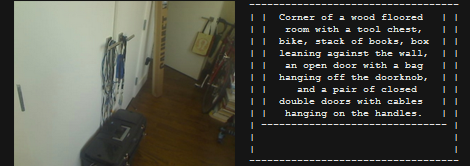
[Matt]’s Descriptive Camera looks just like any other point and shoot camera, albeit a little more boxy and homemade-looking. It even works just like the Polaroids of yesteryear – snap a picture and in a few minutes you’ve got a reproduction in your hands. Unlike any other camera before, [Matt]’s camera doesn’t give you an image. [Matt]’s camera gives you a description of the picture you took, printed out on easily-scrapbooked thermal receipt paper. Yes, mankind is now that meta.
To build the hardware of his camera, [Matt] took a BeagleBone single-board Linux computer and attached a webcam and a thermal receipt printer. The real magic is in the artificial artificial intelligence that is Mechanical Turk. [Matt]’s camera sends his picture up to the Internet where some random stranger describes his picture. This description is sent back and printed on the receipt paper.
Even though [Matt] is spending $1.25 to have a single picture described on Mechanical Turk, there’s probably not another camera as retro-meta-fabulous-fantastic out there.









Recent Comments