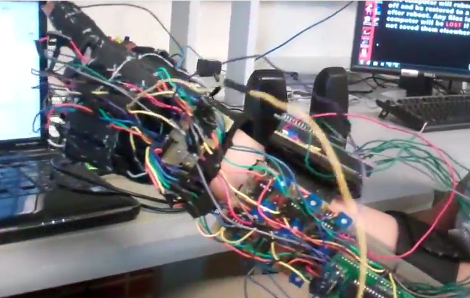
This wire covered glove is capable of turning your hand gestures to speech, and it does so wirelessly. The wide range of sensors include nine flex sensors, four contact sensors, and an accelerometer. The flex sensors do most of the work, monitoring the alignment of the wearer’s finger joints. The contact sensors augment the flex sensor data, helping to differentiate between letters that have similar finger positions. The accelerometer is responsible for decoding movements that go along with the hand positions. They combine to detect all of the letters in the American Sign Language alphabet.
An ATmega644 monitors all of the sensors, and pushes data out through a wireless transmitter. MATLAB is responsible for collecting the data which is coming in over the wireless link. It saves it for later analysis using a Java program. Once the motions have been decoded into letters, they are assembled into sentences and fed into a text-to-speech program.
You’ve probably already guess that there’s a demo video after the break.








Recent Comments