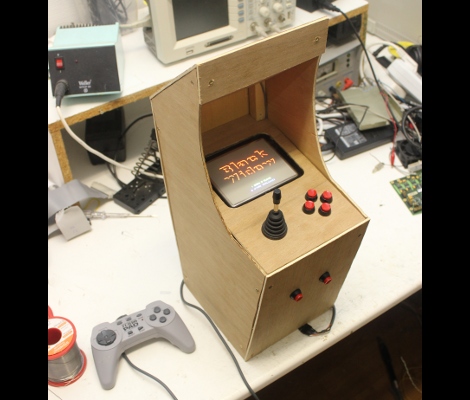

[Sprite_TM] wanted to challenge his VHDL skills, and there’s no more satisfying way of doing this than making something that will be playable when you’re done. He decided to try his hand at creating a vector-based CRT arcade. The distinction here is that vector-based games take control of the magnetic ring that guides the electron path toward the screen. This technique allows point-to-point graphic generation rather than the pixel-based scanning that CRT televisions use.
He had a small color CRT on hand and decided to grab a VHDL version of asteroids from the Internet to see if he could get it to work. But upon further inspection of the source he found that it had a chunk of code which rasterized the vectors for use with a scanning monitor. After removing that chunk, and giving it a spin he had enough confidence that he knew what he was doing to start implementing his own game. The choice of what title really came down to the hardware the original arcade cabinets used. He was not interested in implementing a soft-process for the math chips used in games like Star Wars and Tempest. In the end he got a version of Black Widow up and running, and even built a miniature cabinet for the thing. Check out some of the gameplay in the clip after the break.





Recent Comments