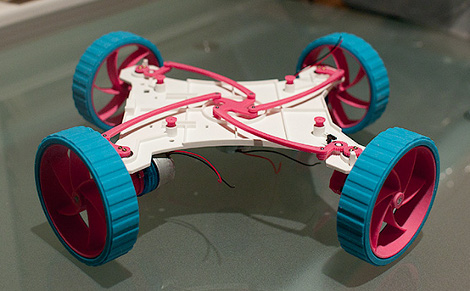
Skills are all that’s needed to solve a problem. Take this four-wheeled robot as an example. [Michal Zalewski] wanted it to be omnidirectional but wasn’t very satisfied with the concept of mecanum wheels and the like. So he designed a chassis with wheels at each corner that can pivot as one to change orientation. The image may look like a rendering at first glance, but this is actually the physical prototype. See what we mean about skills?
Okay, so the robot design is pretty cool. But we’re more excited about the build process. We’ve looked at [Michal’s] work before. He wrote a thorough guide about CNC mold making. These parts are all cast from epoxy. This starts with a rough milled mold, which is given a second pass for the fine details before being painted with a release agent and used to make a silicone mold. From this the parts are produced. Check out the Flickr set showing the casting process for the planetary gear box on each motor. If only these results were as easy to achieve as he makes it look.
[via Reddit]




Just wow!
I just killed an hour on that guide to machining and mold-making. Absolutely fantastic.
The secret sauce seems to be Innovative Polymers IE-3075 to cast the parts. It seems that Innovative Polymers doesn’t sell directly to the public. Anyone know where to actually buy the stuff?
They sell directly (just not online), and also have a list of resellers on the website.
Holy crap Batman! This is some fine engineering and craftsmanship here!!!
BTW: This steering mechanism may already be patented, but I know for sure the wheel concept is patented by iRobot for their PackBots.
http://www.google.com/patents/US6615885
THAT IS AWESOME!!!
Would have been significantly faster and cheaper to just 3d printed it using SLA or polyjet.
maybe… but no where as cool nor precise (to within 3 mils)…
16 microns is not accurate enough?
16 microns = 0.0006299 in
@Hackerspacer LOL. Go on then…
@Hackerspacer, I’d like to see a 3D printer get 16 microns AND still be faster or cheaper than this method… UV Epoxies are not exactly cheap… nor that fast when you have to mold the dozens of parts it takes for just ONE of these gear sets…
You wouldn’t be making MOLDS – you would print the parts directly. No milling, degassing, silicone molding, degassing, casting, curing, removing flash, accounting for shrinkage on the epoxy and silicones – you get the picture. Print it in a UV epoxy, heck even a filled UV cured epoxy. Done.
Method 1)
Come up with STL files -> accounting for shrinkage on the epoxy and silicones -> getting tooling -> milling -> degassing -> silicone molding -> degassing -> casting -> curing -> removing flash -> measuring parts -> done.
Method 2)
Come up with STL files -> Print. Done.
Don’t get me wrong. There is serious artistry here. But you can use another technology and get much quicker and more accurate results – possibly even cheaper as well.
you still haven’t come up with a current example of something that works at better than 3 mils, is cheaper than molding (which is very cheap), is as fast (you make the molds ONCE and with care you can reuse to your hearts content… need to make 4 planetary gear sets? each with a dozen or so pieces? no problem… make one molding and you can then make 4 sets without issue…)
There is a reason that 3D printing still isn’t the main method of plastic forming… it isn’t as cheap nor as fast. I’d dare say even for one offs, not just pieces profiting from the economy of scale.
oh and don’t tell me that your Method 2 is that simple… It takes TONS of tinkering to get 3D prints the way you want them before you can pump them out… Just the same as when you’re molding… it all becomes part of the process.
Still haven’t explained where you’re getting an honest 16 micron resolution from…. or anything like it either 😉
Hackerspacer: I see the sentiment for 3D printing, but the question of accuracy aside, that comparison of workflows is pretty bogus.
First of all, you’re comparing apples to oranges: you can directly machine parts on CNC mills (more so than print them, given the greater choice of engineering-grade materials), but there are clear benefits to moldmaking, and a reason why people buy 3D printers just to make molds. Heck, there are even wax printers that aren’t good for anything else, and they sell for big bucks.
The details of the workflow are also largely bogus. I don’t understand why “measuring parts”, degassing a master mold, or “getting tooling” are on your list. There is usually no practical shrinkage you need to account for in room-temperature polyurethane resins, too: it’s not injection molding.
Consequently, for 3D printing, you usually have multiple additional steps involved, depending on the technology: removing support structures or melting out filler wax, sandblasting the surface, post-curing the resin in SLA systems, etc.
And really – there are probably no sub-$50k 3D printers that can get the detail and accuracy of a $2k mill. Even if they claim a high resolution in X-Y, there’s usually some fine print about the Z axis, or the minimum size of a surface feature they can print. In a couple of years, this will probably change; wax-printing systems are pretty promising, in particular.
Faster than using his CNC to just cut the parts straight out of an easily machinable plastic?
Correct me if I’m wrong, but he chose this method only because he could easily/quickly mold additional units.
I want to be like you when I grow up!! You can tell when someone takes pride and adds a little artistry in their work.
Thank you also for your guides that you have generously taken a lot of time to write. I was just getting ready to bite the bullet and start forking out some cash. Your guides have probably saved me a lot of money and misery.
Please keep us posted!
It will be interesting to see this move with fluid movements rather than: Stop… straighten wheels… move forward… stop… rotate wheels 90 degrees… rotate machine. If it’s even possible.
Very nice.
I imagine if you tried to keep driving the wheels while they rotated you’d get a bit of “skid” steering happening.
If you didn’t continue to drive the wheels and tried to freewheel them, I’m not sure they would freely rotate given the 125:1 gear ratio.
As long as it’s moving it should be able to change configuration easily enough.
I’m guessing that doing all the maths needed for smooth turns will be a lot of work.
U could probably Google all of zee maths on da interwebz, lol.
Rotating wheels try to always keep its original rotation axis, just as a bicicle or a gyroscope works, so there will be a force opposing the direction change and the steering mechanism will have to account for that.
This is pretty cool, but i found his cycloid drive even more interesting (warning: gear porn ahead!) http://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/cycloid/
wow, just WOW… so simple yet complex at the same time
To my eye, this level of work blurs the line between engineering and artistry in a way that is rare and pleasing to encounter. This hacker’s respect for process is admirable. I hope to see some complex segmented joints or something like that in the future.
– Robot
amazing build. kudos to michael and thanks for sharing.
Very cool to see how to go from concept to making it with that precision and the documentation of the process. That´s a direction i want to go as well… one day.
The mars rovers use a similar navigating scheme except this one takes it a step further and can just crab over sideways. Very cool.
Impressive work! I thought it was funny how he shows the miniscule costs of the materials to make the parts after making molds with a $21K milling machine!
Really nice. I would go ahead and add the other two drive motors though if it were me.
Very impressive!
I wonder if the middle motor can be replaced with a servo perhaps. Looking for a video of this in action but didn’t find any. The build is very well documented and the work has so much precision.
Unbelievable. Really great stuff and much better than omnidirectional wheels.
His reasons for not doing an additive process:
http://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/guerrilla_cnc1.shtml
Look under “2. Milling? That’s so old school!”
Definitely one of the best projects I’ve seen on HaD in a long time. Clever idea, and very well executed.
Just absolutely wow! Precise engineering and art in one design. I am a techie, but have worked with artists, and the combination produces some amazing results. This guy is both an engineer AND an artist at the same time, a very powerful combination. I wish you long life and prosperity kind sir, and thank you for sharing with the public!